What is Seaonic?
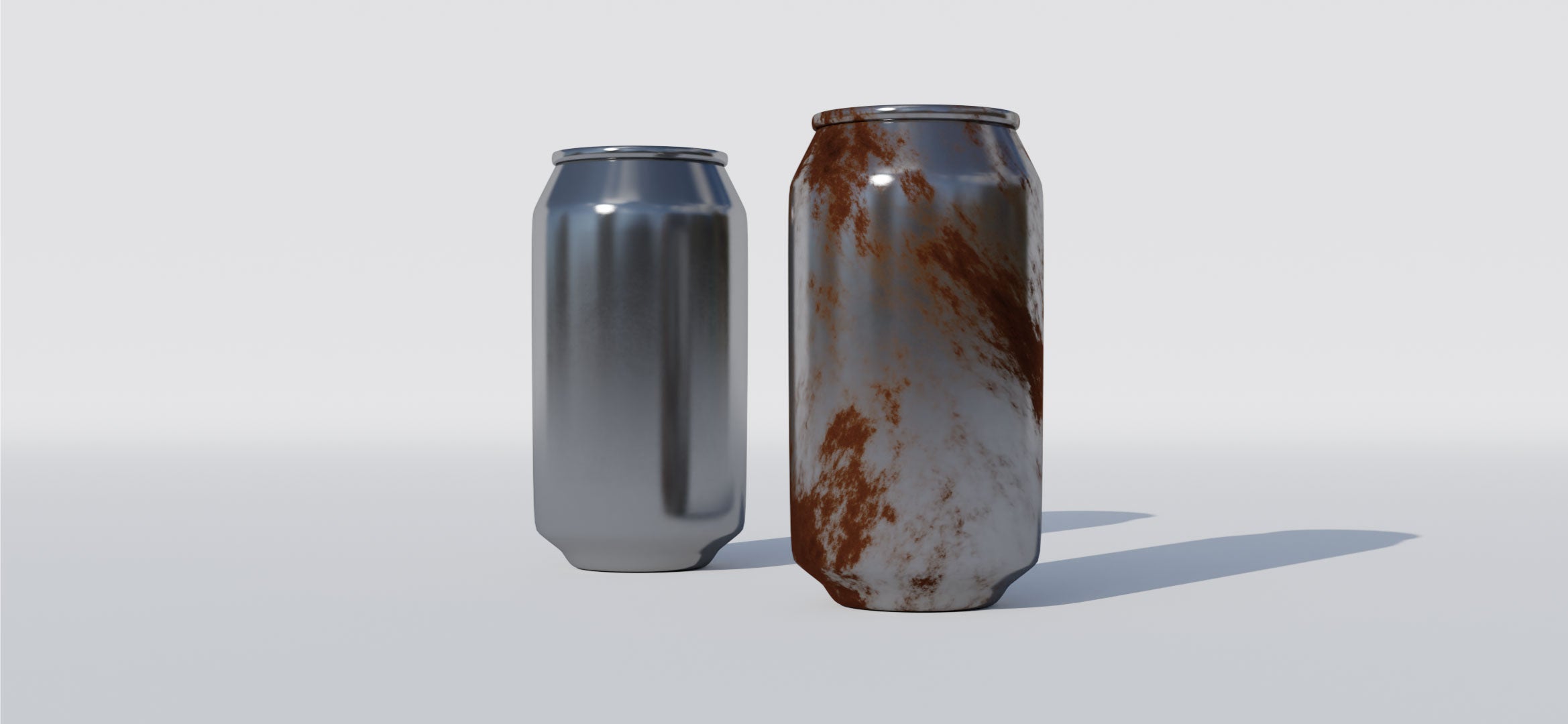

why oxidation is ruining your electrolytes and what you can do
01. what is oxidation?
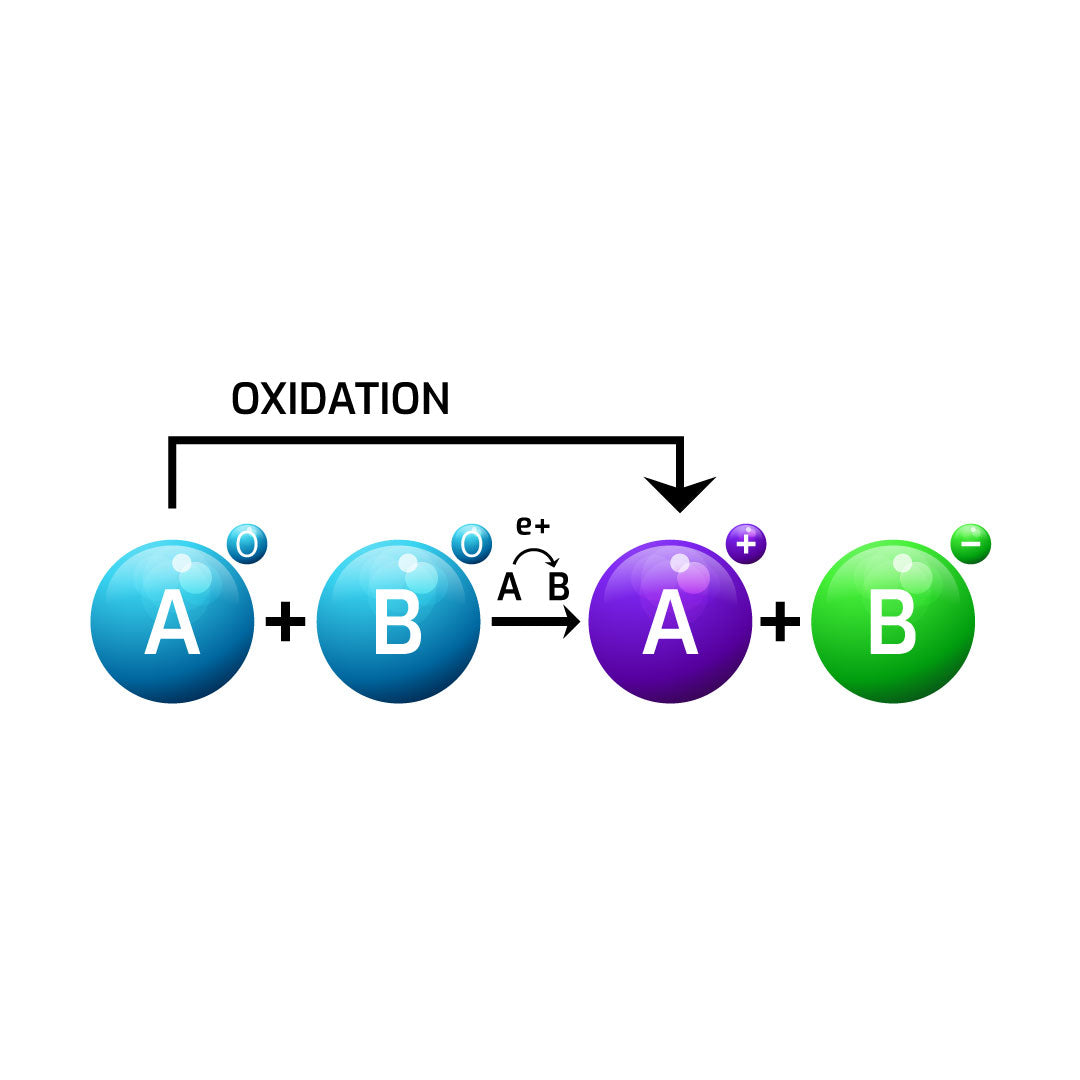
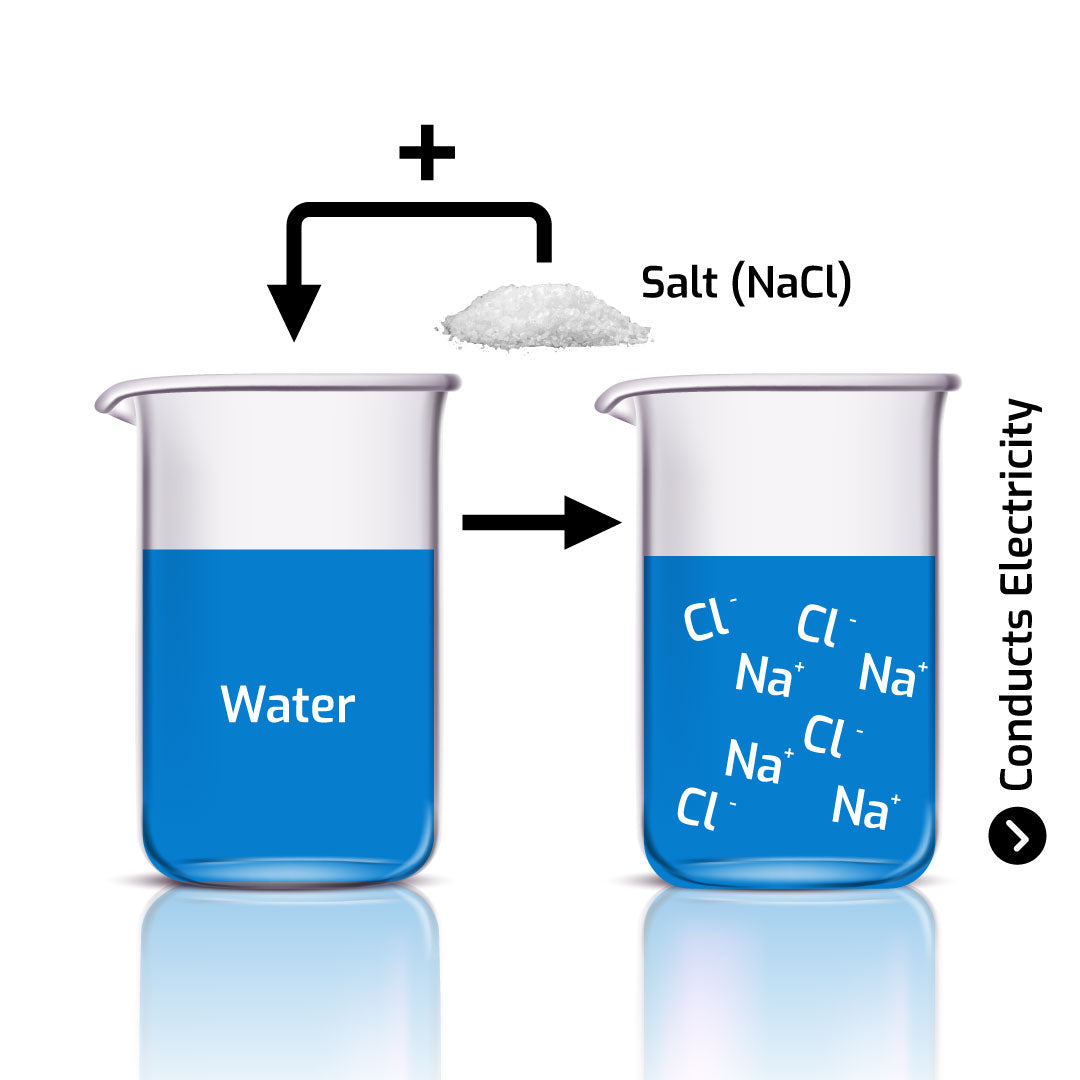
02. salt is corrosive
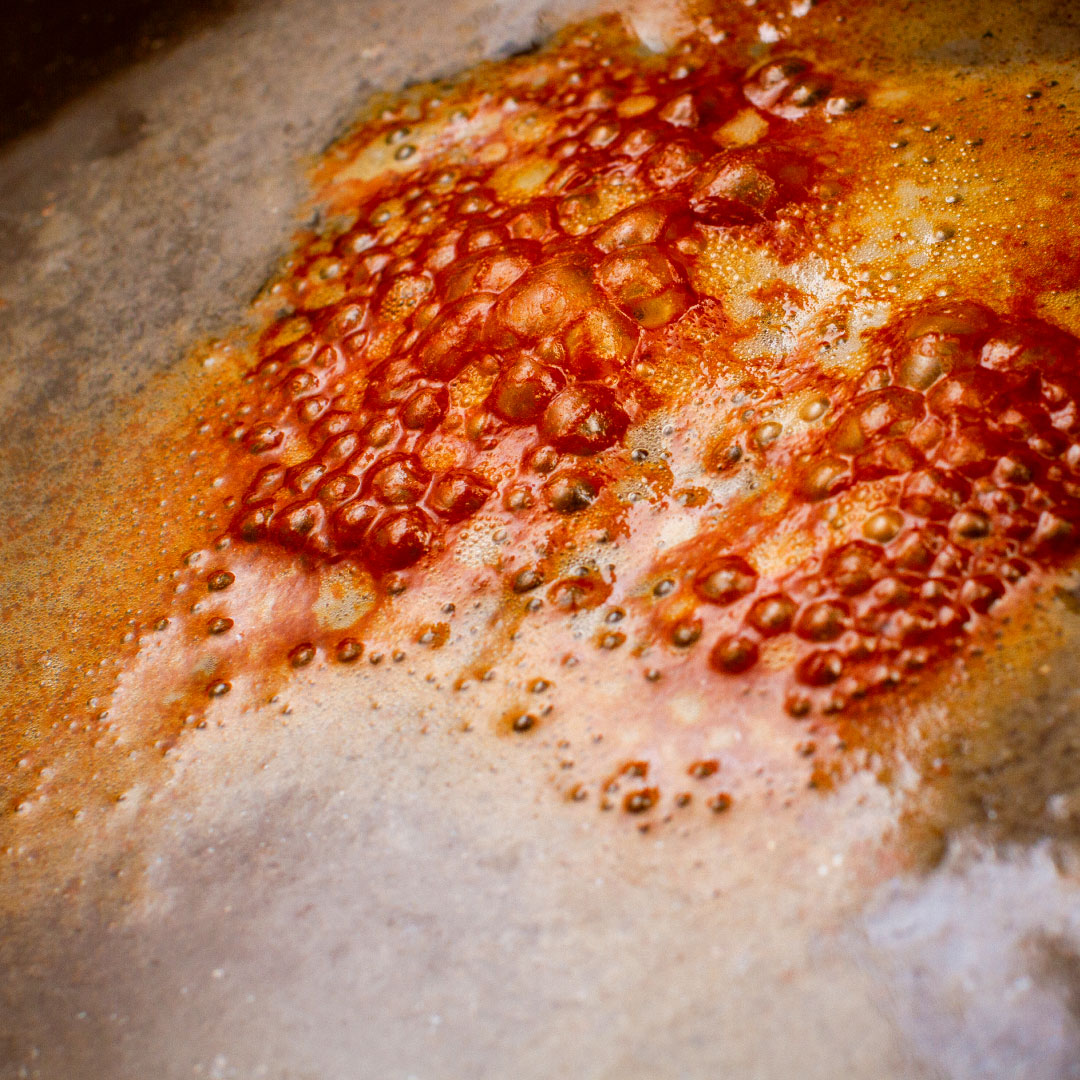

03. why packaging matters

04. what are electrolytes and how do they work?
05. why seaonic stands out

the ultimate electrolyte comparison
seaonic

other electrolytes
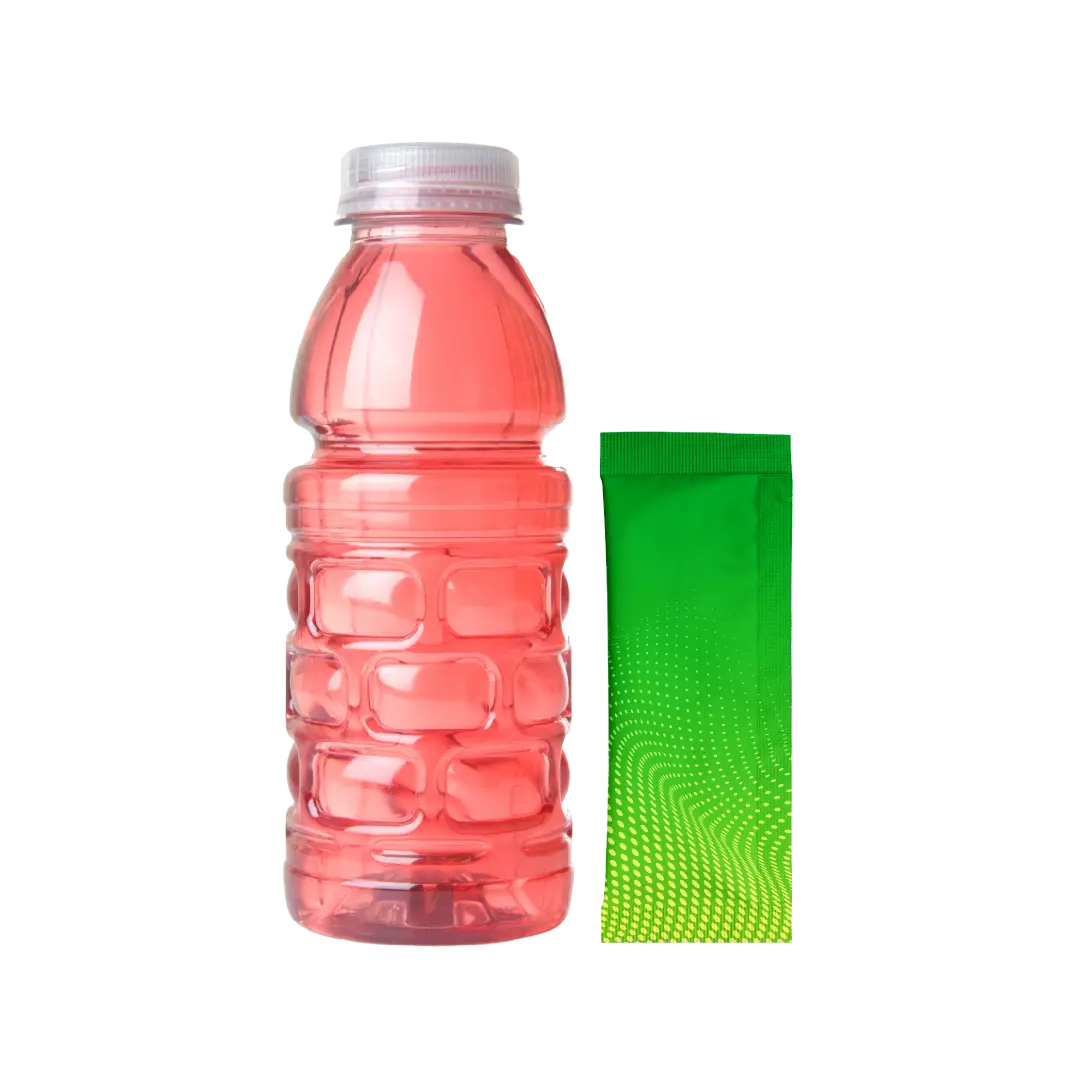

the difference is clear
the ultimate electrolyte comparison
seaonic

other electrolytes













